
Back in the days (as in when we started PCI more than 10 years ago), when it came to testing and scans, there were probably very gray lines on it. We saw a lot of reports that came out under the guise of ‘penetration testing’ that was straight out lifted from an automated Nessus Scan or one of the free Acunetix scans available. The problem was exacerbated when these penetration testing reports were further accepted by regulatory bodies like our regulatory bank and passed by other internal/external auditors. They basically just looked at a report and if it sounded and looked technical enough then it was technical enough.
Now, PCI got the hint and released a few versions of the Penetration Testing Guidance document, the latest iteration on 2017. A big part of it talks about scoping, clarifying on qualifications and requirement 11. But one of the key features of the document is highlighted in 2.1:
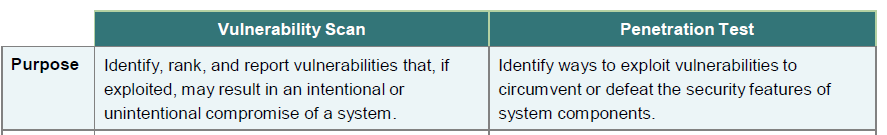
This came about to stem the misconception that as long as you have completed the vulnerability scan, you can use that to pass off as a penetration testing. We still see customers going down this route, in whatever creative ways they can conjure to avoid the penetration testing exercise.
An example was this response on their external PT report stating:
“We have conducted the PT exercise based on the recently passed ASV scan report by the QSA. Since the ASV scan has passed, the penetration testing report is also considered to be passed as there are no vulnerabilities to test.”
Which is basically the philosophy that as long as the scans do not yield any high or medium vulnerabilities, i.e a passing scan, there is no longer a need to conduct any penetration testing. Their concept was simple and fairly understandable: since there are no “vulnerabilities” in the scan, there is nothing for us to ‘test’.
Of course, this was rejected by the QSA.
While there are many arguments on this matter, the simple case against this is: the scan produces potential vulnerabilities and may even miss some out that may not be reported. False negatives do exist even in commercial scanners such Qualys or Nessus (two common auto-scanners). Additionally, a passing scan does not mean no vulnerabilities, it just means there are no medium/high vulnerabilities based on a non-contextual scan to the environment. A non-contextual scan means a lot of scanners already use internal libraries in their scanning database to categorise vulnerabilities without the definition of the actual environment risk it is scanning. So to equate CVSS to the actual risk of the organisation may be too broad an assumption as some low vulnerabilities may still be able to be exploited manually. The classic example here is when we check a simple form entry password and find it is well protected and designed, technically. However, a pentester may then go out into the organisation’s forum and discover that the admin regularly upkeeps a password file in Google Drive and shares it to the entire world inadvertently. The scanner won’t discover things like that.
Therefore to simply state, just because there is a passing ASV scan, it equates to penetration testing passing, is not going to get a free pass in PCI.
Another question that many organisations come back to us, when they have their team of penetration testers doing internal testing is: Well, then how do you do a penetration test, then, if you state we cannot use the ASV report to also pass our external penetration testing?
And it would seem weird, that when I look at them and answer: wouldn’t your penetration testers be able to answer that, instead of us? So from the auditor perspective, we look at 3 things: Tools, Technique, Team.
The tools being used are important, but not all for pentest. Just by stating you have Kali or Metasploit doesn’t necessarily mean you know how to operate it. Technique (or method) is important to document. This is key for PCI and a key difference between hackers and pentesters. A pentester would know how to document each step, inform their client and normalize and not destroy the environment. A hacker (or let’s use the more correct term cracker) would simply go in and cause as much damage as possible, depending on his/her objective. You would rarely come across crackers developing comments and detailed reports/documents to their victims and executive summaries to the Audit Committee justifying their methods, the scope of coverage and the time and date of engagement. And finally, PCI looks at the personnel (or team) conducting the exercise. They may be certified (or not), but they should at least be qualified. In this case, if the pentester has no idea how to start a pentest, then the normal assumption would be — he’s not a pentester. A chef doesn’t ask people how to start cooking. He may require an input or two to understand what he needs to cook, or how spicy the broth should be for the customer; but if the he’s asking how do we start the cooking process or what is a wok, then that should be a red flag.
So, while the coverage of penetration testing and vulnerability scanning in the entire document is not the the purpose of this article, it is keenly important to know the difference between both (penetration test vs vulnerability scan), and not use one to justify the inaction of the other. Your QSA may bounce back that vulnerability scan attempting to disguise itself as a penetration test and waste precious compliance timeline in the process.
Drop us a note at pcidss@pkfmalaysia.com for any queries you have for PCI-DSS or ISMS and we will get back to you straight away! Stay Safe!
